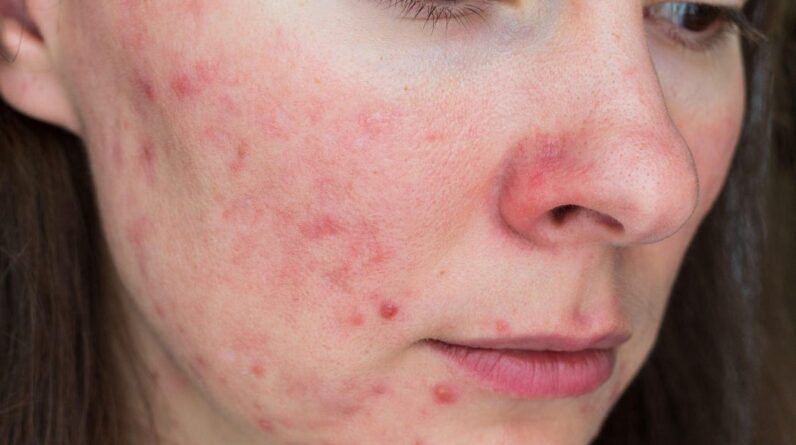
Papulopustular rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the development of papules and pustules on the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead. This condition can be exacerbated by a number of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors. In recent times, prolonged wearing of masks has become a significant factor in the exacerbation of Papulopustular rosacea, especially on the cheeks of the patients. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, and consequences of prolonged mask-wearing on Papulopustular rosacea patients’ cheeks. Additionally, it will provide tips on preventing acne and managing acne-prone skin.
Acne Types and Causes
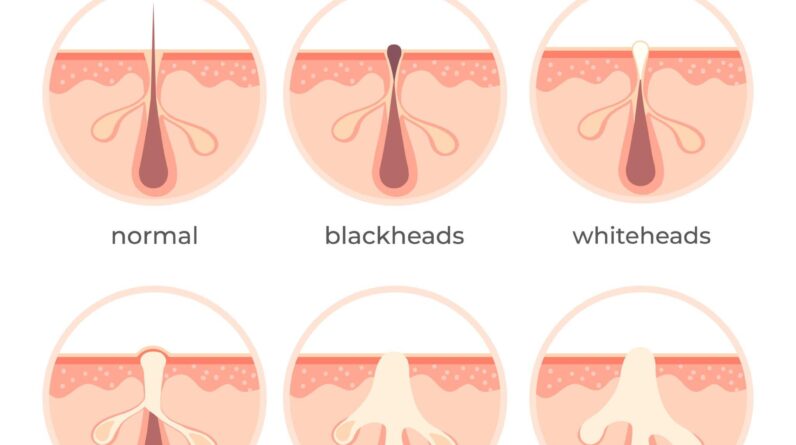
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. There are different types of acne, and Papulopustular rosacea is one of them. Papulopustular rosacea is characterized by the development of small, red bumps (papules) and pus-filled bumps (pustules) on the face, especially the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead. The exact cause of Papulopustular rosacea is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Papulopustular rosacea is often exacerbated by certain triggers, such as alcohol, spicy foods, stress, and sun exposure. In recent times, prolonged wearing of masks has become a significant trigger for Papulopustular rosacea, especially on the cheeks of the patients.
Consequences of Prolonged Wearing of Masks
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the widespread use of masks, which has become a crucial measure in preventing the spread of the virus. However, prolonged wearing of masks can have adverse effects on the skin, especially for those with Papulopustular rosacea. Masks can cause skin irritation, inflammation, and acne breakouts, particularly on the cheeks of the patients.
When wearing a mask, the skin on the cheeks is often subjected to friction, heat, and moisture, which can exacerbate existing Papulopustular rosacea. Friction caused by the mask can cause mechanical trauma to the skin, leading to the development of papules and pustules. Moreover, the heat and moisture trapped under the mask can create an ideal environment for bacterial growth, leading to further inflammation and acne breakouts.
Prolonged wearing of masks can also exacerbate other skin conditions, such as acne vulgaris, seborrheic dermatitis, and perioral dermatitis. These conditions are characterized by the development of acne-like bumps and redness on the face, which can be worsened by the use of masks.
Preventing Acne and Managing Acne-Prone Skin
Preventing acne and managing acne-prone skin requires a holistic approach that addresses both internal and external factors. Here are some tips on how to prevent acne and manage acne-prone skin:
Cleanse the skin regularly
Cleansing the skin twice a day can help remove excess oil, dirt, and impurities that can clog pores and lead to acne breakouts. Use a gentle cleanser that is suitable for acne-prone skin.
Moisturize
Moisturizing the skin can help prevent dryness and flakiness, which can exacerbate acne breakouts. Use a non-comedogenic moisturizer that is suitable for acne-prone skin.
Protect the skin from the sun
Sun exposure can exacerbate acne breakouts and cause hyperpigmentation. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to protect the skin from the sun.
Avoid touching the face
Touching the face can transfer bacteria and dirt to the skin, leading to acne breakouts. Avoid touching the face as much as possible, especially when wearing a mask.
Choose the right mask
Choosing the right mask is crucial in preventing skin irritation and acne breakouts. Opt for masks made of breathable materials, such as cotton, and avoid masks that are too tight or too loose.
Take breaks from wearing a mask
Taking breaks from wearing a mask can help reduce skin irritation and acne breakouts. Take off the mask for a few minutes every hour or so to allow the skin to breathe.
Use acne-fighting ingredients
Acne-fighting ingredients, such as salicylic acid and benzoyl peroxide, can help prevent and treat acne breakouts. Use products that contain these ingredients in moderation, as they can cause dryness and irritation if overused.
Conclusion
Papulopustular rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that can be exacerbated by a number of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Prolonged wearing of masks has become a significant factor in the exacerbation of Papulopustular rosacea, especially on the cheeks of the patients. Masks can cause skin irritation, inflammation, and acne breakouts, particularly on the cheeks. Preventing acne and managing acne-prone skin requires a holistic approach that addresses both internal and external factors. Following the tips provided in this article can help prevent acne breakouts and manage acne-prone skin, especially for those with Papulopustular rosacea.